Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) redefines traditional security by never inherently trusting any user or system, regardless of their position inside or outside the network. This blog post explores the implementation of Zero Trust Architectures for applications, a critical security framework in today's digital threat landscape.
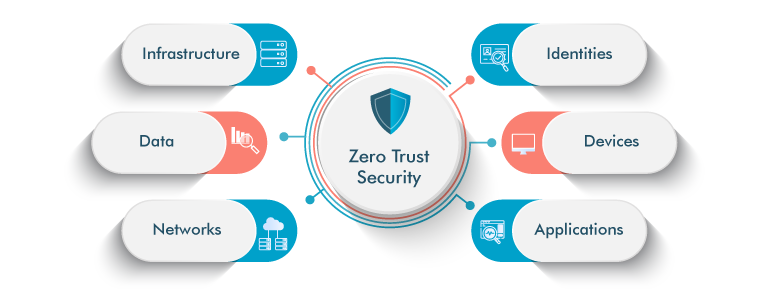

What is Zero Trust Architecture?
Zero Trust Architectures represent a paradigm shift in security, challenging the default trust accorded to users and systems in traditional models. At its core, ZTA advocates for continuous verification and strict access control, irrespective of the user's network position. This approach is vital as organizations confront escalating digital threats and seek robust security solutions.
Zero Trust Architectures Market Trend
By 2032, the Zero Trust Architecture market is projected to reach approximately USD 118.5 billion, growing at a CAGR of 16.78% from 2023 to 2032. North America currently leads with the largest market share. This growth is fueled by a rising need for more effective security measures in response to the increasing frequency and complexity of digital threats.
Zero Trust Security Market Size, 2022 to 2032 (USD Billion)
The expansion of the zerotrust security market is primarily driven by the increasing frequency and complexity of digital threats. As traditional security models, particularly those based on perimeter defenses, become less effective against sophisticated attacks, organizations are urgently turning towards the zero trust model. It responds to emerging threats and has a proactive strategy to strengthen digital defences.
Zero Trust Network Architecture Evolution
The evolution of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) can be attributed to its proactive stance and adaptability, making it a suitable solution for a variety of environments, including on-premises, cloud, and hybrid networks.
- Zero trust network architecture has gained prominence due to escalating digital threats, such as advanced persistent threats (APTs) and ransomware, revealing limitations in traditional security models.
- ZTA represents a proactive security approach, emphasizing continuous verification, least privileged access, and micro-segmentation to address digital threats' dynamic and evolving nature.
- The flexibility of ZTA makes it suitable for securing enterprise networks across various environments, including on-premises, cloud, and hybrid setups.
- The successful implementation of ZTA results in enhanced security posture and reduced risk, contributing to its reputation as a proven security model and driving its overall popularity and adoption.

Strategies for Successful Zero Trust Architecture
Establishing a Zero Trust Architecture effectively involves adhering to several key principles, each contributing to a robust and secure network environment where trust is continuously verified, not assumed.

- Verify Identity: ZTA mandates robust authentication mechanisms, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), to confirm the legitimacy of users and devices.
- Least Privilege Access: Users and devices are granted minimal access, minimizing potential damage in case of a security breach.
- Micro-Segmentation: Network segmentation limits lateral movement during security incidents, with isolated segments enforcing strict access controls.
- Continuous Monitoring: ZTA emphasizes real-time user and device behavior monitoring, promptly addressing anomalies and potential threats.
- Encryption: Protect data communications within the network through robust encryption, preventing unauthorized data access.
- Policy Enforcement: Establish and rigorously enforce access policies tailored to user roles and specific contextual factors across all network areas.
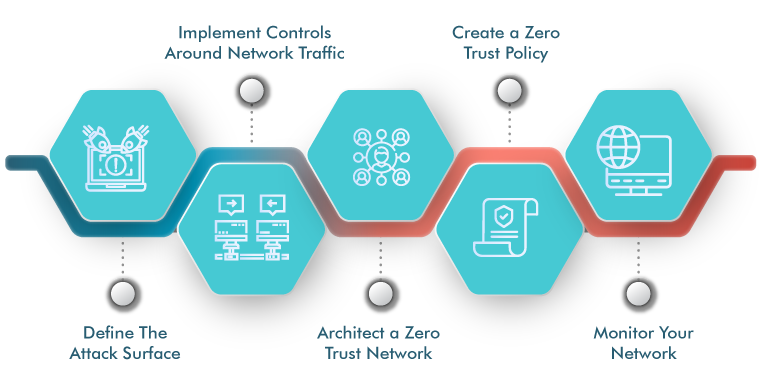
Implementation of a Zero Trust Network Architecture
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture is not just a theoretical concept; it's a proactive strategy that involves strategic steps to strengthen an organization's security posture.
- Foundation Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive security evaluation to identify and categorize organizational assets based on criticality to understand current vulnerabilities and risks.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Implementing robust security measures, such as deploying multi-factor authentication (MFA) and establishing detailed access controls to adhere to the principle of least privilege.
- Network Segmentation: Strategically divide the network into isolated segments, restricting lateral movement during security incidents, with access policies based on specific needs.
- Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response: Utilize real-time monitoring tools to oversee user and device activities, coupled with a responsive incident response plan for swift action against irregularities.
- Encryption Protocols: Robust encryption protocols are deployed to secure communication between users, devices, and network segments, with regular updates to adapt to evolving security requirements.
- Policy Enforcement Mechanisms: Establishing and consistently enforcing access policies, incorporating user roles, device types, and contextual factors while conducting regular audits to ensure policy adherence and making necessary adjustments.
- Integration of ZTA in Cloud Environments: Extend ZTA principles to cloud environments, ensuring cloud-based applications and resources receive the same level of security as on-premises solutions.
5 Steps to Zero Trust Implementation
Challenges in Implementing a Zero Trust Security Architecture
While zero trust security architecture (ZTA) offers significant security enhancements, its implementation comes with several challenges that organizations need to navigate:
Complex Implementation
Transitioning to ZTA can be complex, involving intricate configurations and potential operational disruptions.
Resource Requirements
ZTA demands considerable financial and human resources, which can be particularly challenging for smaller organizations with limited budgets.
Impact on User Experience
The strict access controls and ongoing verification processes essential to ZTA might impact the user experience, potentially causing frustration or resistance.
Legacy System Integration
Aligning ZTA with older legacy systems can be difficult due to potential incompatibilities in architecture and functionality.
Monitoring Demands
The continuous monitoring required for ZTA is resource-intensive and can challenge the maintenance of real-time network activity oversight.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring ZTA aligns with various regulatory standards can be complex, as specific regulations may not directly correspond with zero trust principles.
Role of QASource
At QASource, we excel at turning theoretical security concepts into practical, actionable strategies, particularly in Zero Trust Security Architecture. Our expertise is demonstrated through:
-
Comprehensive Risk Evaluations
We conduct in-depth assessments to identify vulnerabilities and risks within your organization.
-
Asset Categorization
We assist in classifying organizational assets by their criticality, ensuring targeted protection strategies.
-
Robust Authentication Measures
Our team implements strong authentication mechanisms, such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and sets up detailed access controls in line with the least privilege principle.
-
Network Segmentation
We aid in dividing networks into isolated segments to control access and movement, which is particularly important during security incidents.
-
Cloud Integration
By extending ZTA principles to cloud environments, we ensure consistent security levels for both on-premises and cloud-based resources.
Our approach ensures a comprehensive, secure implementation of a Zero Trust Architecture tailored to each organization's unique needs.
Conclusion
Zero Trust Architectures represent a significant shift in digital security, marking a transformative and progressively evolving journey. This approach, which redefines trust from fundamental principles to practical implementation, is increasingly adopted and supported by significant tech players. Characterized by its proactive nature, flexibility, and growing recognition within regulatory frameworks, ZTA has become an essential element in contemporary digital defense strategies.



