According to a new report by Juniper Research, more than 33 billion records will be stolen by cybercriminals by 2023, which is an increase of 175% from 2018. The role of effective cybersecurity testing, hence, becomes even more important than ever. It protects all categories of data like sensitive data, personally identifiable information, protected health information, personal financial information, and intellectual property from theft and damage. Cyber threats can come from any level of your organization, so it becomes a must to educate your people about some common cyber threats like social engineering scams, phishing, ransomware attacks, and other attack vectors designed to steal intellectual property or personal data.
What Is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practice of securing computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks. It aims to scale back the danger of cyberattacks and make a shield against the unauthorized exploitation of systems and networks.
What Are the Types of Cybersecurity?
Let us now look at the various types of cybersecurity services:
-
Network Security
Network security involves addressing vulnerabilities affecting your operating systems and network architecture, including servers and hosts, firewalls, wireless access points, and network protocols. Network security acts as a wall between your network and malicious activity and being an organization, you have to protect your network so you can constantly deliver services to meet the demands of your customers and protect your reputation as a business.
-
Cloud Security
Cloud security is concentrated around securing data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud. It mainly focuses on the vulnerabilities coming from internet services and shared environments. Cloud security protects the infrastructure and application security from cloud-connected components.
-
IoT (Internet of Things) Security
IoT devices include everything that connects to the Internet without human intervention, such as smart fire alarms, lights, thermostats, and other appliances. IoT security involves securing these smart devices and networks connected to the IoT.
-
Application Security
Application security involves addressing vulnerabilities resulting from insecure development processes in designing, coding, and publishing software or an application.
-
Cybersecurity Infrastructure
Organizations need to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to manage their security risks. Organizations that rely on critical infrastructure should understand the liabilities and ensure protection against it. Attackers can aim at your utility systems to attack your business, so it becomes a must to evaluate how it can affect you and develop a contingency plan.
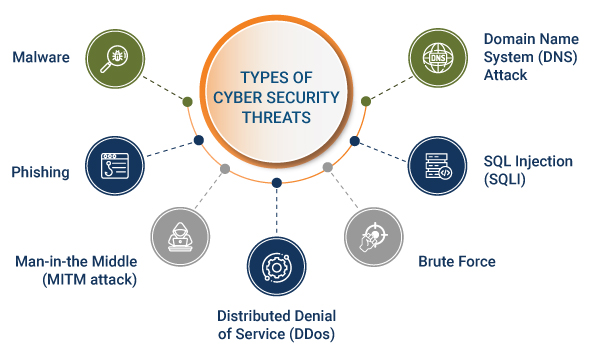
Common Cybersecurity Threats
Here are the different types of commonly used cyber threats:
-
Malware
Malicious software variants such as viruses, Trojans, and spyware that provide unauthorized access or cause damage to a computer are called malware. Malware, once activated, can block access to key network components, install additional harmful software, obtain information by transmitting data from the hard drive, and disrupt individual parts, making the system inoperable.
-
Ransomware
It is a kind of malware that locks down files, data, or systems. It threatens to erase or destroy the data or leak private or sensitive data to the public.
-
Phishing and Social Engineering
It is a sort of social engineering that tricks users into providing their sensitive information. Phishing emails or text messages appear to be from a legitimate user asking for sensitive information, such as credit card data or login information.
-
Insider Threats
Former employees, business partners, contractors, or anyone who has had access to systems or networks in the past can be considered an insider threat if they abuse their access permissions.
-
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
A DDoS attack attempts to crash a server, website, or network by overloading it with traffic, usually from multiple coordinated systems. Cyber attackers often use a flood attack to disrupt the “handshake” process and carry out a DoS attack. Several other techniques are also used and some cyber attackers use the time that a network is disabled to launch other attacks. Methods of DDoS attacks include Botnets, Smurf attacks, and TCP SYN flood attacks.
-
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
An intruder infiltrates a system and remains undetected for an extended period. The intruder leaves the networks and systems intact so that he can spy to steal sensitive data while avoiding the activation of defensive countermeasures. Common indicators of an APT presence include new account creation, abnormal activity, backdoor/trojan horse malware, odd database activity, and unusual data files.
-
Man-in-The-middle Attacks
Man-in-the-middle is an eavesdropping attack, where a cybercriminal intercepts and relays messages between two parties to steal data. These attacks occur when a user uses an unsecured public Wi-fi network. In this type of attack, attackers insert themselves between the visitor and the network and then use malware to install software and use data maliciously. MITM attacks include session hijacking, replay attacks, IP spoofing, eavesdropping attack, and Bluetooth attacks.
-
DNS Attack
A DNS attack is a misuse that could allow an attacker to exploit Domain Name System (DNS) vulnerabilities, meaning it would route the communication to a website based on the hacker's exploit.
-
Injections
An injection is an attack on the application’s database using any query language to gain information or execute actions that normally would require an authenticated user account.
-
Brute Force
A brute-force attack consists of an attacker that submits many passwords or passphrases with the hope of eventually guessing correctly.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity Implementation
The following best practices can help your organization implement a strong cybersecurity process that can reduce your vulnerability to cyber attacks and protect your critical information systems, without intruding on the user.
-
Update Your Software and OS
If you get instructions for security updates, install them right away. This should also apply to personal devices you use at work. Installing updates instantly helps you defend against the latest cyber threats.
-
Use Anti-virus Software
Use Security solutions that can detect and remove threats. Antivirus should be installed on your systems.
-
Use Strong Passwords
Ensure your used application passwords can’t be easily figured out. Appropriately follow the password rules. Use a strong password that should contain at least 10 characters, numbers, symbols, and capital and lowercase letters. A good practice is to change your passwords regularly.
-
Never Open Email Attachments From Unknown Senders
You should not open email attachments received from unknown senders. These could be infected with malware and can harm your system or destroy user data.
-
Never Click on Unreliable Links
Beware of phishing attacks. Hackers try to trick you into clicking on a link that could result in a security breach. Phishers hope that the user will open pop-up windows or other malicious links that could contain viruses or any malware embedded into them. It becomes really important that you should be cautious of links and attachments in emails from senders you don’t recognize. After just one click, you could enable phishers to infiltrate your organization’s network.
-
Avoid Using Unsecured WiFi Networks in Public Places
Insecure networks leave you vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks. Office Wi-fi networks should be secure and encrypted. If you are working remotely, you can help protect data by using a virtual private network. VPN is very essential when you are doing work outside of the office. Public Wi-fi networks can be risky and these networks make your data vulnerable.
-
Enable Firewall Protection at Work and Home
Having a firewall for the company network and your home network is the first line of defense in helping protect data against cyberattacks. Firewalls prevent unauthorized users from accessing your websites, mail services, and other sources of information that can be accessed from the web.
-
Embrace Education and Training
Companies take the time to train their employees. It becomes your responsibility to be aware of your company’s cybersecurity policies and what is expected of you. It is important to learn the process for allowing IT to connect to your devices, along with basic computer hardware terms. That awareness can save time when you contact the support team and they need quick access, and information to resolve an issue.
How QASource Can Help You With Your Cybersecurity Testing Efforts
Our security testing specialists use a range of methods to ensure that the software or application for our clients has been fully tested using the most recent tools and procedures. When it comes to consumer data protection, a security software manufacturer must adhere to several legislative requirements. QASource assists the team in navigating the necessary criteria, ensuring that their product checked each box and remained compliant.
QASource’s security testing methodology involves:
- Evaluating the security of your application concerning current real-world assaults using several manual ways
- Exposing holes in your application's security design
- Detecting security flaws due to implementation flaws
- Exposing flaws resulting from the application's interaction with the rest of your IT architecture
- Increasing total application security while increasing end-user confidence
Conclusion
A vulnerability is a weakness or flaw in the software, hardware, or organizational processes, which when compromised by a threat, can result in a security breach. However, cybersecurity protects the privacy of data and hardware that handles, store, and transmit that data. Cybersecurity penetration testing is an extremely critical aspect of any application, which needs to be tested carefully. QASource has cybersecurity QA engineers who have extensive experience in cybersecurity penetration testing, which has helped many customers in releasing a secure product. You can get a range of cybersecurity services at QASource. To know more about cybersecurity outsourcing and the related services, contact QASource now.

